Write a program in C to find the inverse of the given matrix.
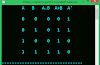
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int m[3][3],m1[3][3],b1[3][3]; int A11,A12,A13,A21,A22,A23,A31,A32,A33; int i,j,a1=0,ai; clrscr(); printf("Enter 3*3 size of matrix:-\n"); for(i=0;i<3;i++) for(j=0;j<3;j++) { scanf("%d",&m[i][j]); } a1=m[0][0]*(m[1][1]*m[2][2]-m[1][2]*m[2][1])-m[0][1]*(m[1][0]*m[2][2]-m[1][2]*m[2][0])+m[0][2]*(m[1][0]*m[2][1]-m[1][1]*m[2][0]); printf("\n|A|!=%d",a1); if(a1==0) printf(" |A|=0 ,\n\tTherefore this matrix is not inverse "); else { A11=m[1][1]*m[2][2]-m[1][2]*m[2][1]; A12=-(m[1][0]*m[2][2]-m[1][2]*m[2][0]); A13=m[1][0]*m[2][1]-m[1][1]*m[2][0]; printf("\n The cofactor of the elements of the first row of |A| are %d %d %d respectively.",A11,A12,A13); A21=-(m[0][1]*m[2][2]-m[0][2]*m[2][1]); A22=m[0][0]*m[2][2]-m[0][2]*m[2][0]; A23=-(m[0][0]*m[2][1]-m[0][1]*m[2][0]); printf("\nThe cofactor of the elements of the second row of |A| are %d %d %d respectively.",A21,A22,A23); A31=m[0][1]*m[1][2]-m[0][2]*m[1][1]; A32=-(m[0][0]*m[1][2]-m[0][2]*m[1][0]); A33=m[0][0]*m[1][1]-m[0][1]*m[1][0]; printf("\nThe cofactor of the elements of the first row of |A| are %d %d %d respectively.",A31,A32,A33); printf("\nThe matrix B whose elements are the cofactor of the elements of |A| is "); printf("\nB=\n"); printf("\t %d %d %d \n",A11,A12,A13); printf("\t %d %d %d \n",A21,A22,A23); printf("\t %d %d %d \n",A31,A32,A33); printf("\nHence adj A =Transpose of B\n"); printf(" %d %d %d \n",A11,A21,A31); printf(" %d %d %d \n",A12,A22,A32); printf(" %d %d %d \n",A13,A23,A33); printf("\nA inverse=\n"); printf("%d/%d %d/%d %d/%d \n",A11,a1,A21,a1,A31,a1); printf("%d/%d %d/%d %d/%d \n",A12,a1,A22,a1,A32,a1); printf("%d/%d %d/%d %d/%d \n",A13,a1,A23,a1,A33,a1); } getch(); }Output:-
Related programs:




0 Comments